iSarcasm: A Dataset of Intended Sarcasm
Silviu Oprea, Walid Magdy
Resources and Evaluation Long Paper
Session 2A: Jul 6
(08:00-09:00 GMT)

Session 3A: Jul 6
(12:00-13:00 GMT)

Abstract:
We consider the distinction between intended and perceived sarcasm in the context of textual sarcasm detection. The former occurs when an utterance is sarcastic from the perspective of its author, while the latter occurs when the utterance is interpreted as sarcastic by the audience. We show the limitations of previous labelling methods in capturing intended sarcasm and introduce the iSarcasm dataset of tweets labeled for sarcasm directly by their authors. Examining the state-of-the-art sarcasm detection models on our dataset showed low performance compared to previously studied datasets, which indicates that these datasets might be biased or obvious and sarcasm could be a phenomenon under-studied computationally thus far. By providing the iSarcasm dataset, we aim to encourage future NLP research to develop methods for detecting sarcasm in text as intended by the authors of the text, not as labeled under assumptions that we demonstrate to be sub-optimal.
You can open the
pre-recorded video
in a separate window.
NOTE: The SlidesLive video may display a random order of the authors.
The correct author list is shown at the top of this webpage.
Similar Papers
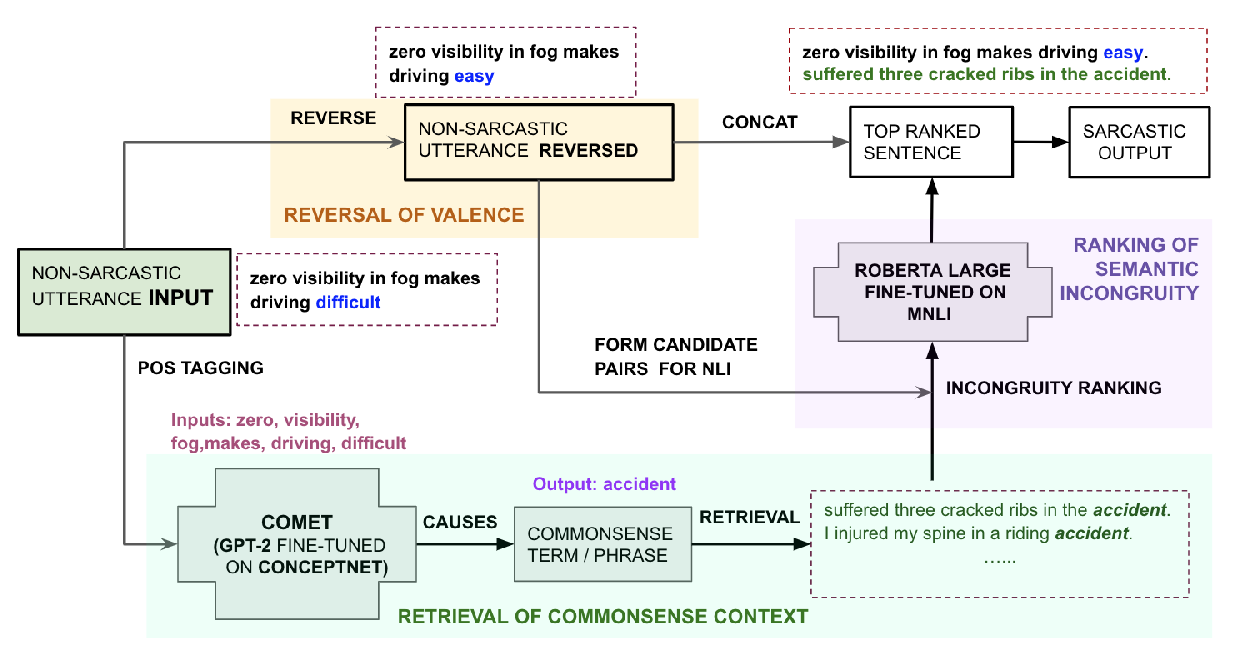
R^3: Reverse, Retrieve, and Rank for Sarcasm Generation with Commonsense Knowledge
Tuhin Chakrabarty, Debanjan Ghosh, Smaranda Muresan, Nanyun Peng,
Reasoning with Multimodal Sarcastic Tweets via Modeling Cross-Modality Contrast and Semantic Association
Nan Xu, Zhixiong Zeng, Wenji Mao,

Sentiment and Emotion help Sarcasm? A Multi-task Learning Framework for Multi-Modal Sarcasm, Sentiment and Emotion Analysis
Dushyant Singh Chauhan, Dhanush S R, Asif Ekbal, Pushpak Bhattacharyya,
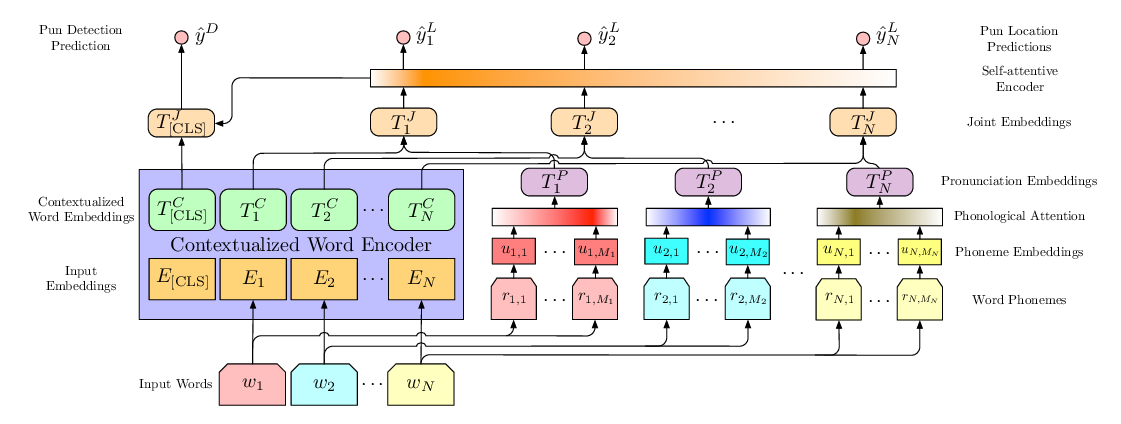
"The Boating Store Had Its Best Sail Ever": Pronunciation-attentive Contextualized Pun Recognition
Yichao Zhou, Jyun-Yu Jiang, Jieyu Zhao, Kai-Wei Chang, Wei Wang,