Distinguish Confusing Law Articles for Legal Judgment Prediction
Nuo Xu, Pinghui Wang, Long Chen, Li Pan, Xiaoyan Wang, Junzhou Zhao
NLP Applications Long Paper
Session 6A: Jul 7
(05:00-06:00 GMT)

Session 7B: Jul 7
(09:00-10:00 GMT)

Abstract:
Legal Judgement Prediction (LJP) is the task of automatically predicting a law case’s judgment results given a text describing the case’s facts, which has great prospects in judicial assistance systems and handy services for the public. In practice, confusing charges are often presented, because law cases applicable to similar law articles are easily misjudged. To address this issue, existing work relies heavily on domain experts, which hinders its application in different law systems. In this paper, we present an end-to-end model, LADAN, to solve the task of LJP. To distinguish confusing charges, we propose a novel graph neural network, GDL, to automatically learn subtle differences between confusing law articles, and also design a novel attention mechanism that fully exploits the learned differences to attentively extract effective discriminative features from fact descriptions. Experiments conducted on real-world datasets demonstrate the superiority of our LADAN.
You can open the
pre-recorded video
in a separate window.
NOTE: The SlidesLive video may display a random order of the authors.
The correct author list is shown at the top of this webpage.
Similar Papers
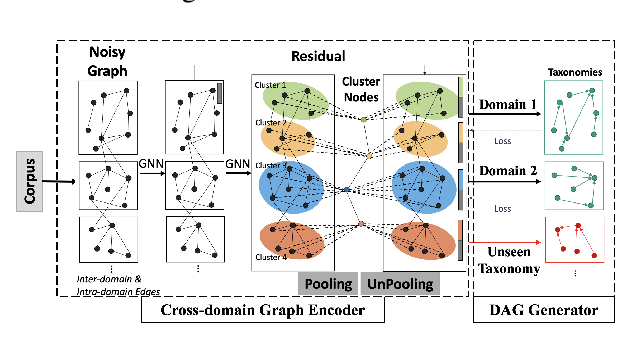
Taxonomy Construction of Unseen Domains via Graph-based Cross-Domain Knowledge Transfer
Chao Shang, Sarthak Dash, Md. Faisal Mahbub Chowdhury, Nandana Mihindukulasooriya, Alfio Gliozzo,
Identifying Principals and Accessories in a Complex Case based on the Comprehension of Fact Description
Yakun Hu, Zhunchen Luo, Wenhan Chao,
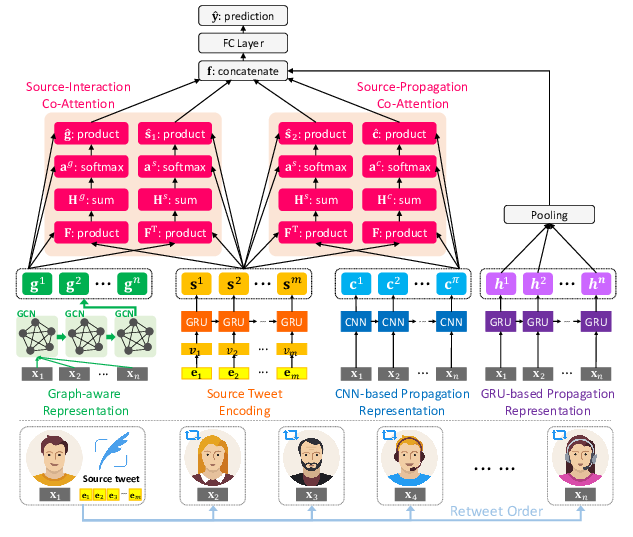
GCAN: Graph-aware Co-Attention Networks for Explainable Fake News Detection on Social Media
Yi-Ju Lu, Cheng-Te Li,
How Does NLP Benefit Legal System: A Summary of Legal Artificial Intelligence
Haoxi Zhong, Chaojun Xiao, Cunchao Tu, Tianyang Zhang, Zhiyuan Liu, Maosong Sun,