Iterative Edit-Based Unsupervised Sentence Simplification
Dhruv Kumar, Lili Mou, Lukasz Golab, Olga Vechtomova
Generation Long Paper
Session 14A: Jul 8
(17:00-18:00 GMT)

Session 15A: Jul 8
(20:00-21:00 GMT)

Abstract:
We present a novel iterative, edit-based approach to unsupervised sentence simplification. Our model is guided by a scoring function involving fluency, simplicity, and meaning preservation. Then, we iteratively perform word and phrase-level edits on the complex sentence. Compared with previous approaches, our model does not require a parallel training set, but is more controllable and interpretable. Experiments on Newsela and WikiLarge datasets show that our approach is nearly as effective as state-of-the-art supervised approaches.
You can open the
pre-recorded video
in a separate window.
NOTE: The SlidesLive video may display a random order of the authors.
The correct author list is shown at the top of this webpage.
Similar Papers
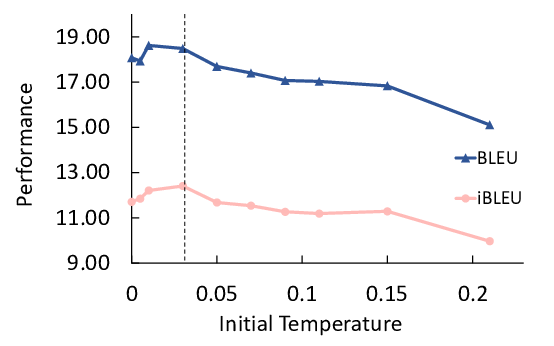
Unsupervised Paraphrasing by Simulated Annealing
Xianggen Liu, Lili Mou, Fandong Meng, Hao Zhou, Jie Zhou, Sen Song,
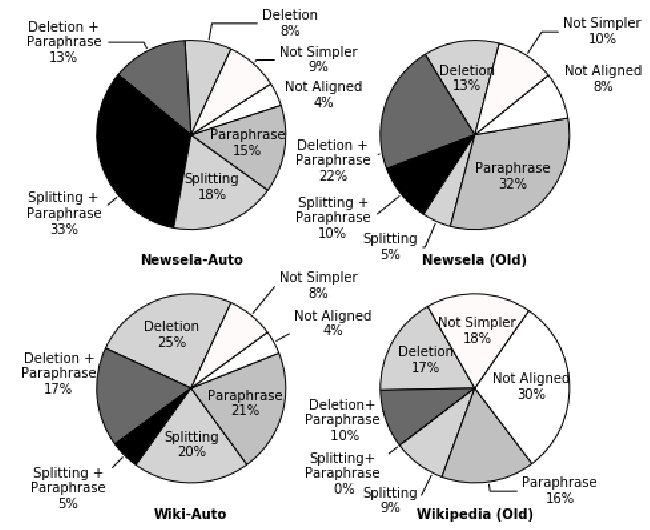
Neural CRF Model for Sentence Alignment in Text Simplification
Chao Jiang, Mounica Maddela, Wuwei Lan, Yang Zhong, Wei Xu,
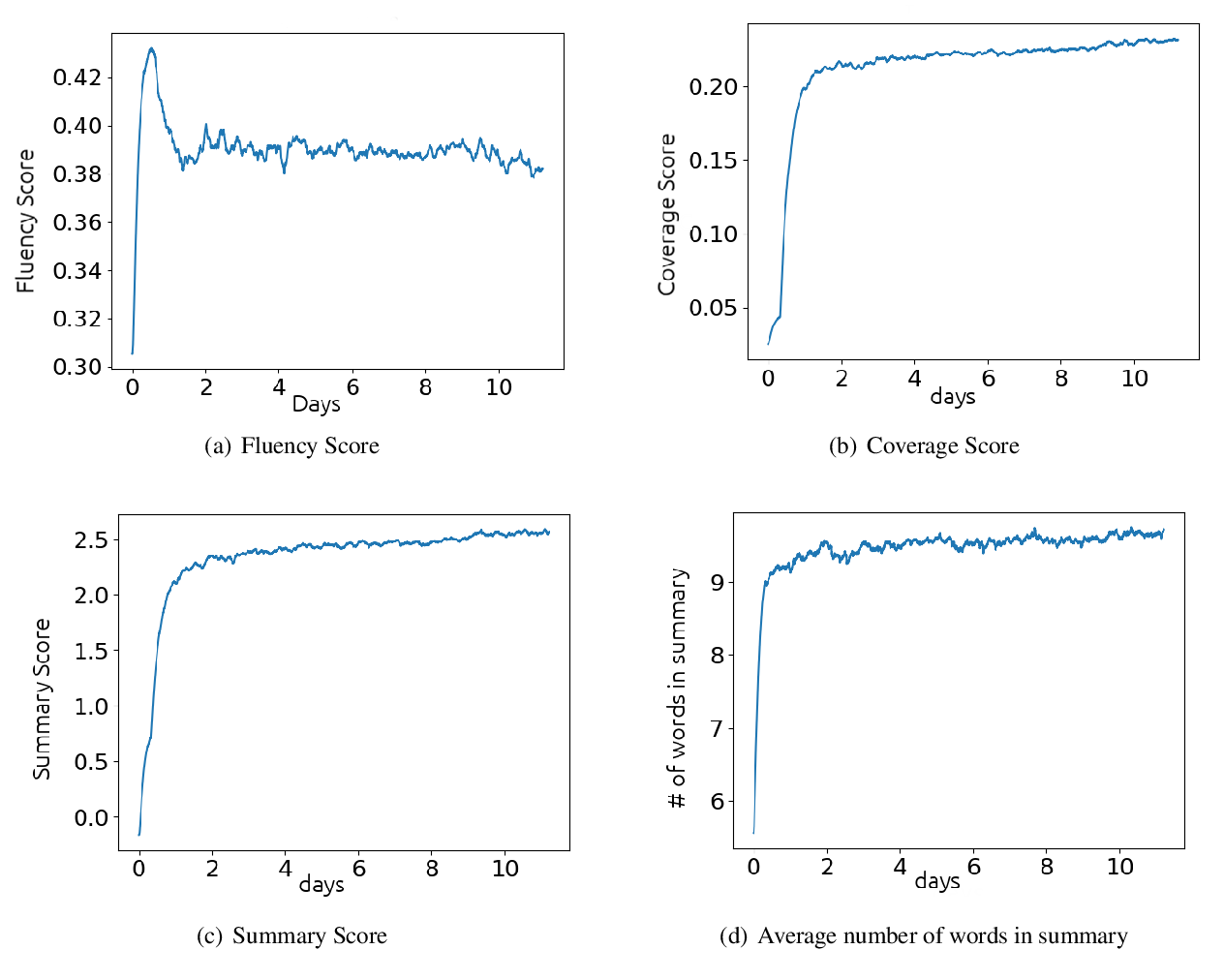
The Summary Loop: Learning to Write Abstractive Summaries Without Examples
Philippe Laban, Andrew Hsi, John Canny, Marti A. Hearst,
ASSET: A Dataset for Tuning and Evaluation of Sentence Simplification Models with Multiple Rewriting Transformations
Fernando Alva-Manchego, Louis Martin, Antoine Bordes, Carolina Scarton, Benoît Sagot, Lucia Specia,