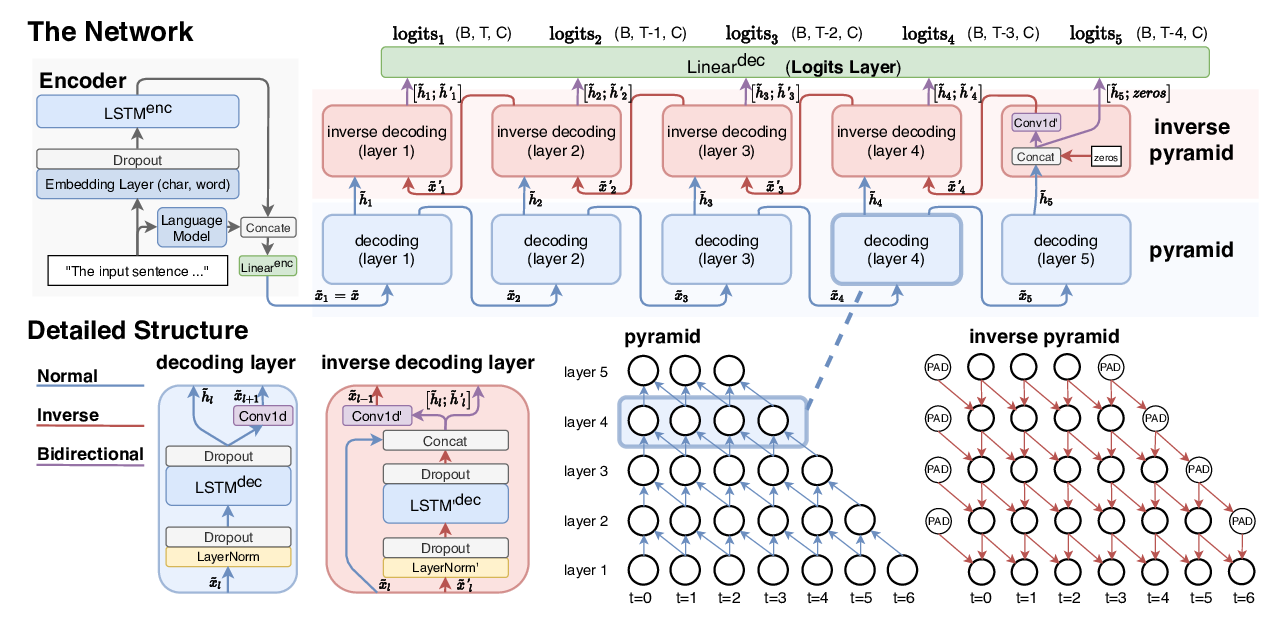
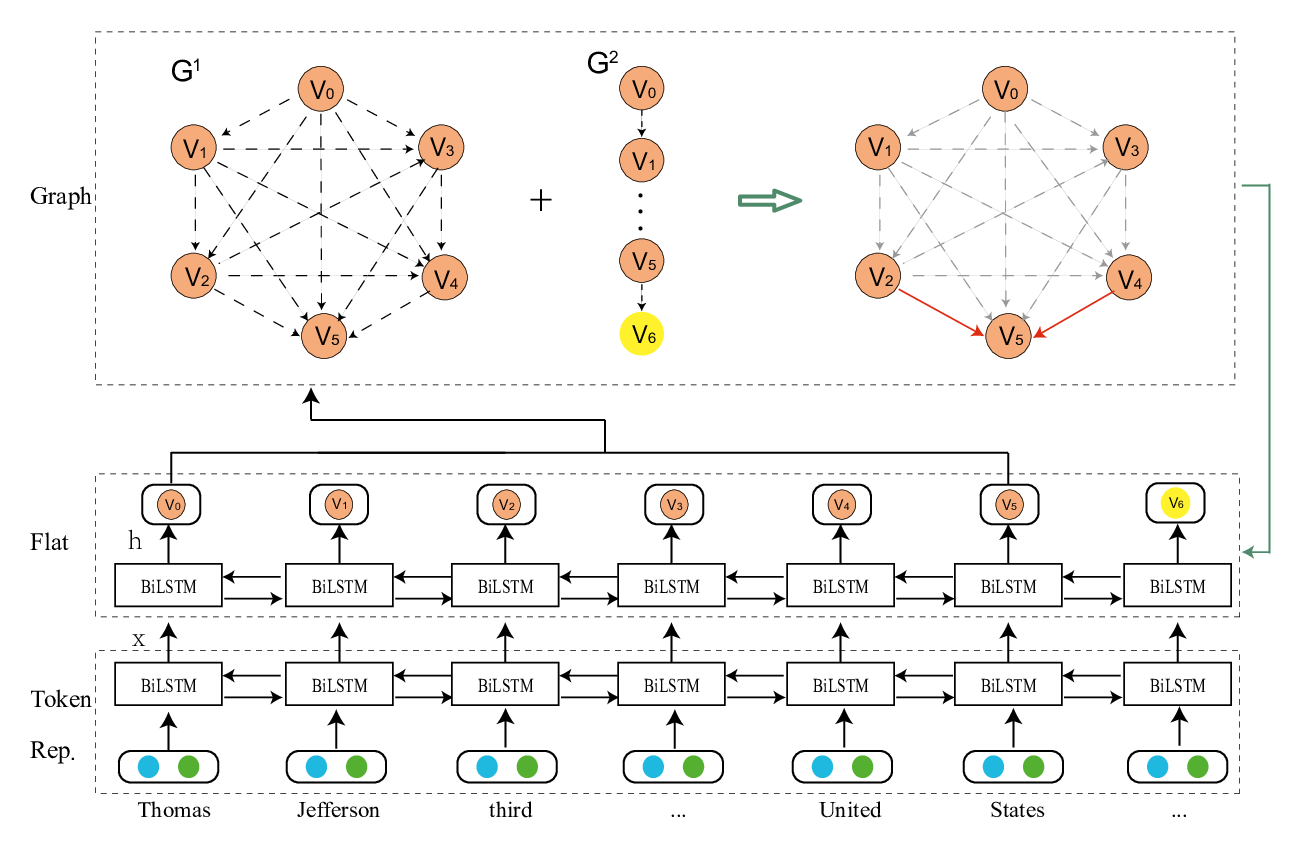
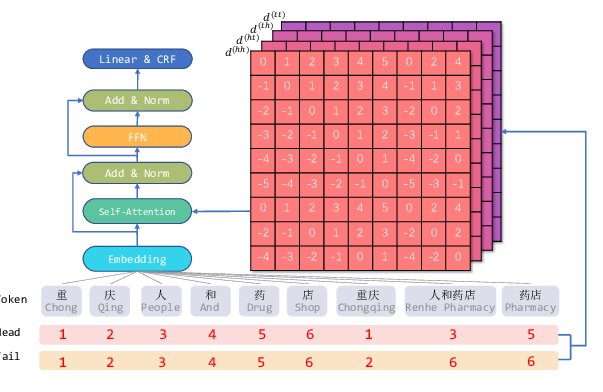
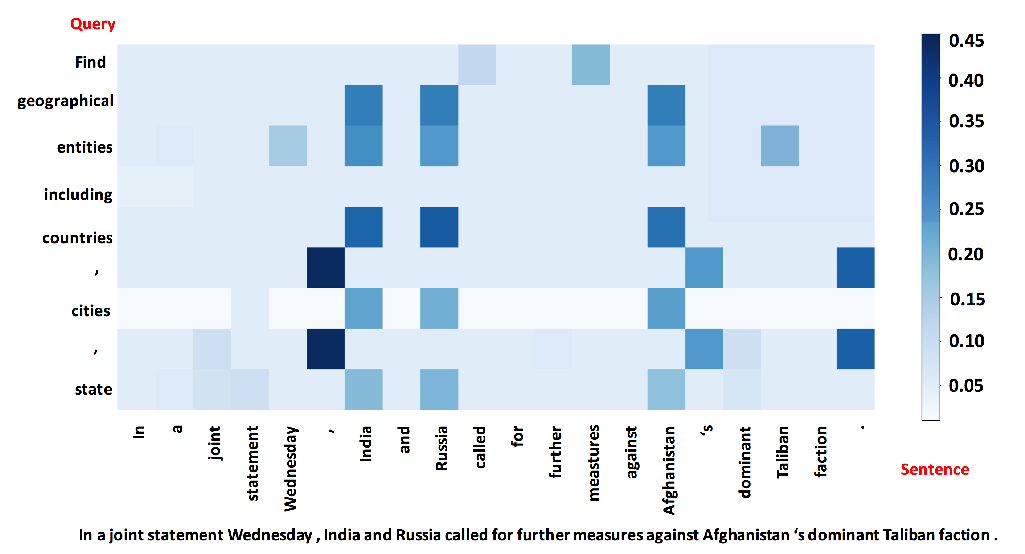
Named Entity Recognition as Dependency Parsing
Juntao Yu, Bernd Bohnet, Massimo Poesio
Information Extraction Short Paper
Session 11B: Jul 8
(06:00-07:00 GMT)

Session 12B: Jul 8
(09:00-10:00 GMT)

Abstract:
Named Entity Recognition (NER) is a fundamental task in Natural Language Processing, concerned with identifying spans of text expressing references to entities. NER research is often focused on flat entities only (flat NER), ignoring the fact that entity references can be nested, as in [Bank of [China]] (Finkel and Manning, 2009). In this paper, we use ideas from graph-based dependency parsing to provide our model a global view on the input via a biaffine model (Dozat and Manning, 2017). The biaffine model scores pairs of start and end tokens in a sentence which we use to explore all spans, so that the model is able to predict named entities accurately. We show that the model works well for both nested and flat NER through evaluation on 8 corpora and achieving SoTA performance on all of them, with accuracy gains of up to 2.2 percentage points.
You can open the
pre-recorded video
in a separate window.
NOTE: The SlidesLive video may display a random order of the authors.
The correct author list is shown at the top of this webpage.
Similar Papers
A Unified MRC Framework for Named Entity Recognition
Xiaoya Li, Jingrong Feng, Yuxian Meng, Qinghong Han, Fei Wu, Jiwei Li,
Pyramid: A Layered Model for Nested Named Entity Recognition
Jue Wang, Lidan Shou, Ke Chen, Gang Chen,