Parsing into Variable-in-situ Logico-Semantic Graphs
Yufei Chen, Weiwei Sun
Semantics: Sentence Level Long Paper
Session 11B: Jul 8
(06:00-07:00 GMT)

Session 13A: Jul 8
(12:00-13:00 GMT)

Abstract:
We propose variable-in-situ logico-semantic graphs to bridge the gap between semantic graph and logical form parsing. The new type of graph-based meaning representation allows us to include analysis for scope-related phenomena, such as quantification, negation and modality, in a way that is consistent with the state-of-the-art underspecification approach. Moreover, the well-formedness of such a graph is clear, since model-theoretic interpretation is available. We demonstrate the effectiveness of this new perspective by developing a new state-of-the-art semantic parser for English Resource Semantics. At the core of this parser is a novel neural graph rewriting system which combines the strengths of Hyperedge Replacement Grammar, a knowledge-intensive model, and Graph Neural Networks, a data-intensive model. Our parser achieves an accuracy of 92.39% in terms of elementary dependency match, which is a 2.88 point improvement over the best data-driven model in the literature. The output of our parser is highly coherent: at least 91% graphs are valid, in that they allow at least one sound scope-resolved logical form.
You can open the
pre-recorded video
in a separate window.
NOTE: The SlidesLive video may display a random order of the authors.
The correct author list is shown at the top of this webpage.
Similar Papers
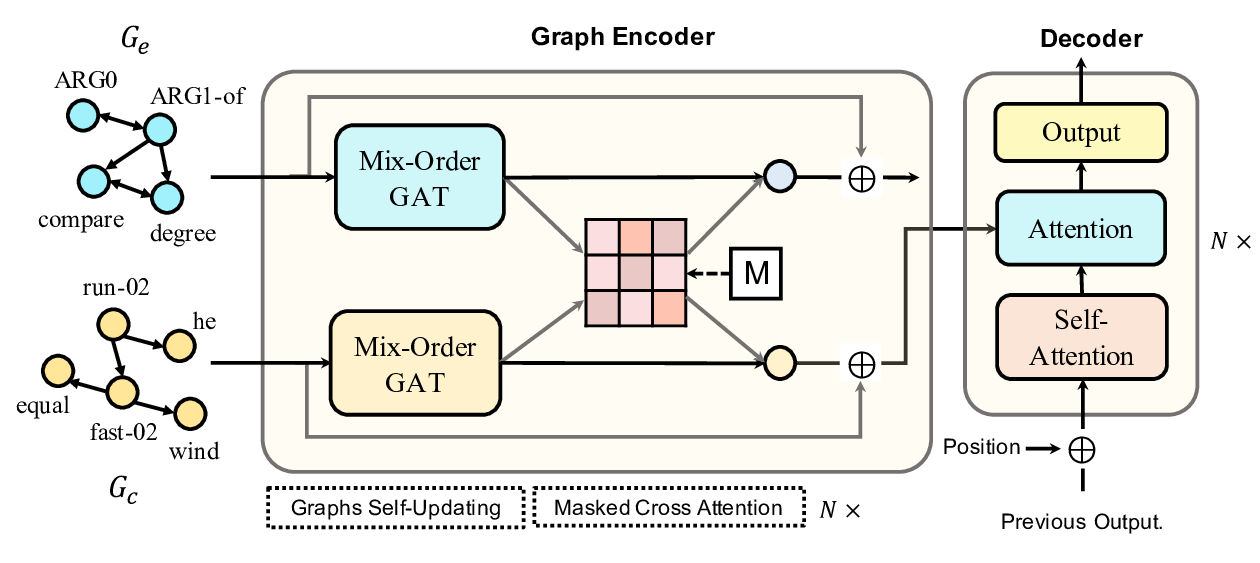
Line Graph Enhanced AMR-to-Text Generation with Mix-Order Graph Attention Networks
Yanbin Zhao, Lu Chen, Zhi Chen, Ruisheng Cao, Su Zhu, Kai Yu,
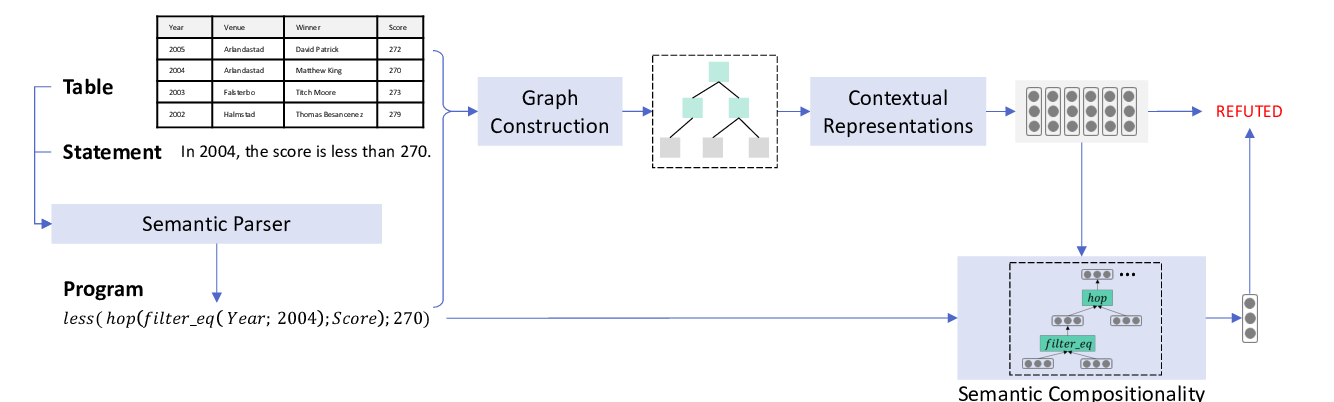
LogicalFactChecker: Leveraging Logical Operations for Fact Checking with Graph Module Network
Wanjun Zhong, Duyu Tang, Zhangyin Feng, Nan Duan, Ming Zhou, Ming Gong, Linjun Shou, Daxin Jiang, Jiahai Wang, Jian Yin,
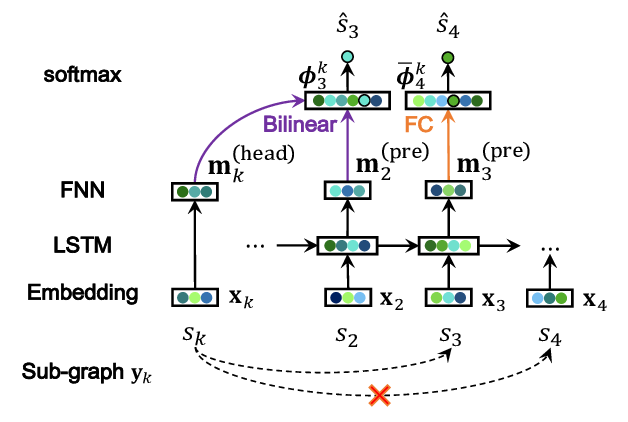
Semi-Supervised Semantic Dependency Parsing Using CRF Autoencoders
Zixia Jia, Youmi Ma, Jiong Cai, Kewei Tu,
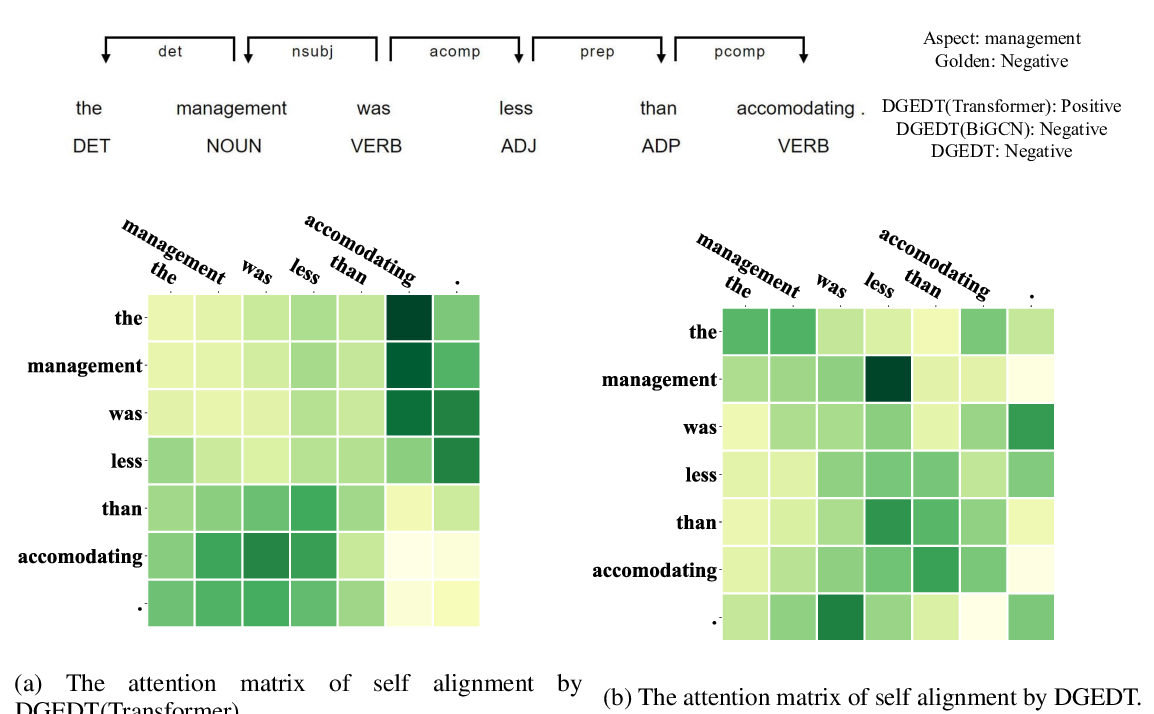
Dependency Graph Enhanced Dual-transformer Structure for Aspect-based Sentiment Classification
Hao Tang, Donghong Ji, Chenliang Li, Qiji Zhou,