A Frame-based Sentence Representation for Machine Reading Comprehension
Shaoru Guo, Ru Li, Hongye Tan, Xiaoli Li, Yong Guan, Hongyan Zhao, Yueping Zhang
Question Answering Short Paper
Session 1B: Jul 6
(06:00-07:00 GMT)

Session 2A: Jul 6
(08:00-09:00 GMT)

Abstract:
Sentence representation (SR) is the most crucial and challenging task in Machine Reading Comprehension (MRC). MRC systems typically only utilize the information contained in the sentence itself, while human beings can leverage their semantic knowledge. To bridge the gap, we proposed a novel Frame-based Sentence Representation (FSR) method, which employs frame semantic knowledge to facilitate sentence modelling. Specifically, different from existing methods that only model lexical units (LUs), Frame Representation Models, which utilize both LUs in frame and Frame-to-Frame (F-to-F) relations, are designed to model frames and sentences with attention schema. Our proposed FSR method is able to integrate multiple-frame semantic information to get much better sentence representations. Our extensive experimental results show that it performs better than state-of-the-art technologies on machine reading comprehension task.
You can open the
pre-recorded video
in a separate window.
NOTE: The SlidesLive video may display a random order of the authors.
The correct author list is shown at the top of this webpage.
Similar Papers
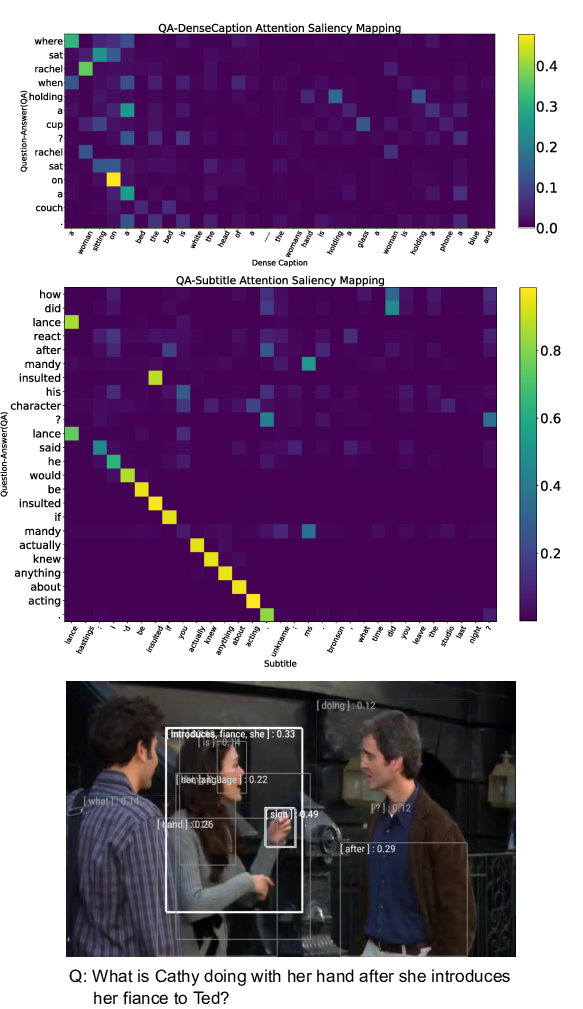
Dense-Caption Matching and Frame-Selection Gating for Temporal Localization in VideoQA
Hyounghun Kim, Zineng Tang, Mohit Bansal,
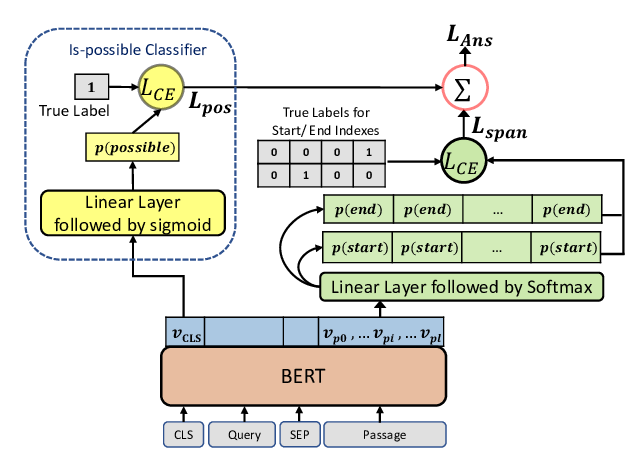
Span Selection Pre-training for Question Answering
Michael Glass, Alfio Gliozzo, Rishav Chakravarti, Anthony Ferritto, Lin Pan, G P Shrivatsa Bhargav, Dinesh Garg, Avi Sil,
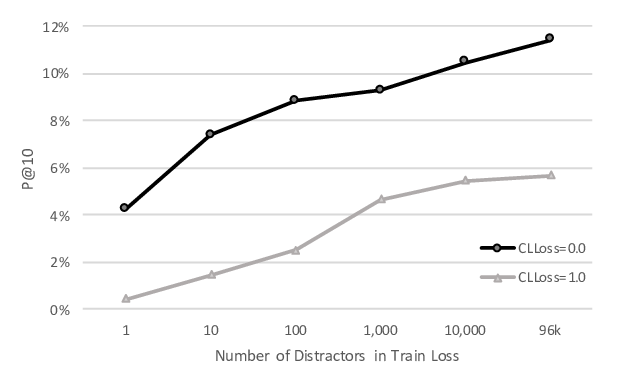
Toward Better Storylines with Sentence-Level Language Models
Daphne Ippolito, David Grangier, Douglas Eck, Chris Callison-Burch,
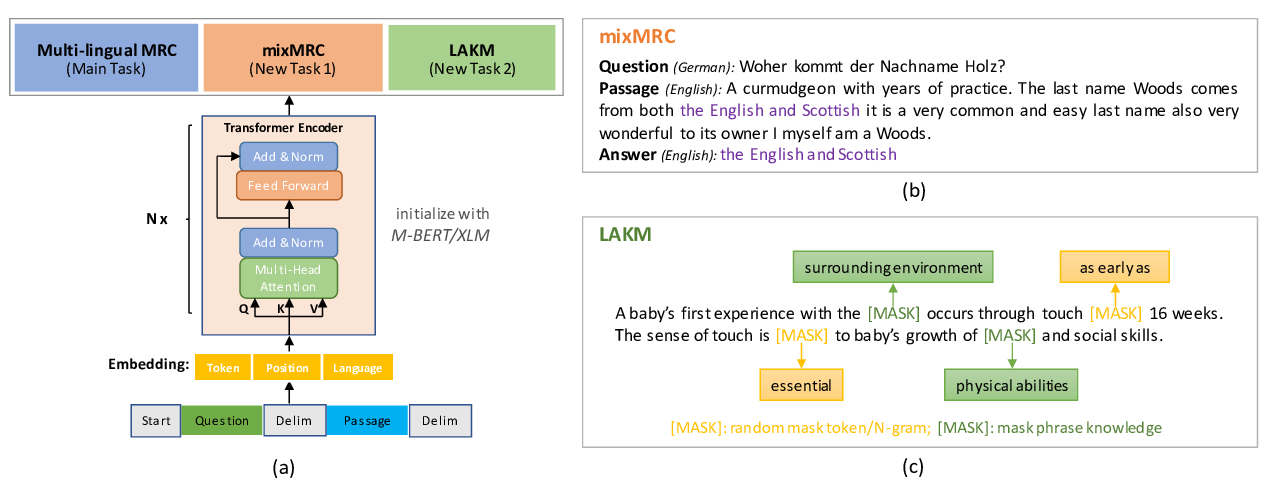
Enhancing Answer Boundary Detection for Multilingual Machine Reading Comprehension
Fei Yuan, Linjun Shou, Xuanyu Bai, Ming Gong, Yaobo Liang, Nan Duan, Yan Fu, Daxin Jiang,