Research Replication Prediction Using Weakly Supervised Learning
Tianyi Luo, Xingyu Li, Hainan Wang, Yang Liu
Student Research Workshop SRW Paper
Session 4A: Jul 6
(17:00-18:00 GMT)

Session 9B: Jul 7
(18:00-19:00 GMT)

Abstract:
Knowing whether a published research result can be replicated or not is important. Carrying out direct replication of published research incurs high cost. It is therefore desirable to have a machine learning aided automatic prediction of a result's replicability. Such predictions can provide a confidence score for each article which can further provide guidelines for spot-checks.Since we will only have access to a small size of annotated dataset to train a machine predictor, we explore the possibility of using weakly supervised learning approaches to improve the prediction accuracy of research replication using both labelled and unlabelled datasets based on text information of research papers. Our experiments over real-world datasets show that much better prediction performance can be obtained compared to the supervised models utilizing only a small size of labelled dataset.
You can open the
pre-recorded video
in a separate window.
NOTE: The SlidesLive video may display a random order of the authors.
The correct author list is shown at the top of this webpage.
Similar Papers
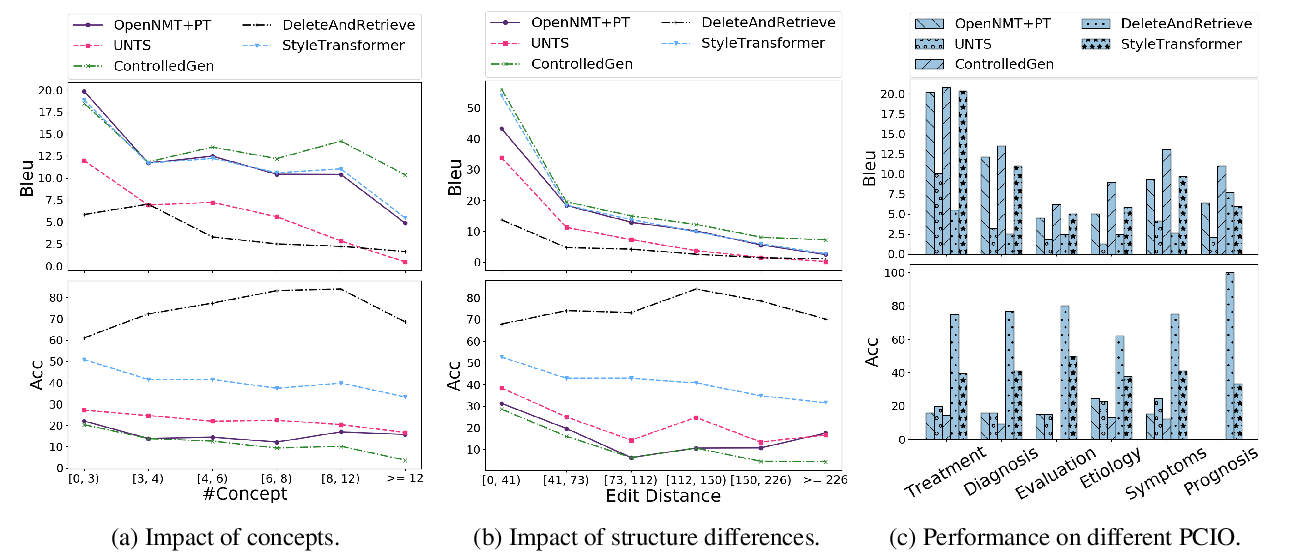
Expertise Style Transfer: A New Task Towards Better Communication between Experts and Laymen
Yixin Cao, Ruihao Shui, Liangming Pan, Min-Yen Kan, Zhiyuan Liu, Tat-Seng Chua,
Will-They-Won't-They: A Very Large Dataset for Stance Detection on Twitter
Costanza Conforti, Jakob Berndt, Mohammad Taher Pilehvar, Chryssi Giannitsarou, Flavio Toxvaerd, Nigel Collier,

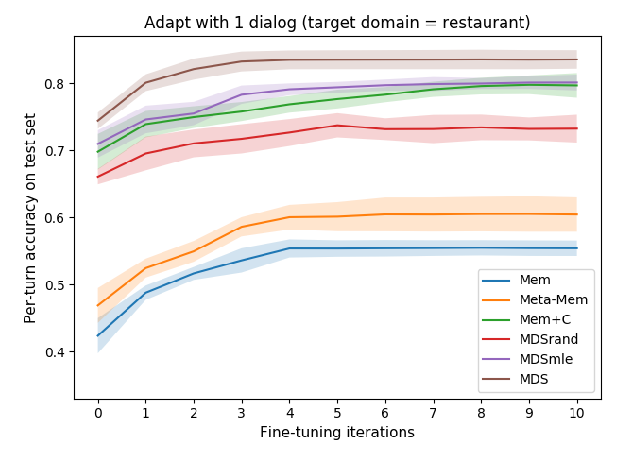
Learning Low-Resource End-To-End Goal-Oriented Dialog for Fast and Reliable System Deployment
Yinpei Dai, Hangyu Li, Chengguang Tang, Yongbin Li, Jian Sun, Xiaodan Zhu,
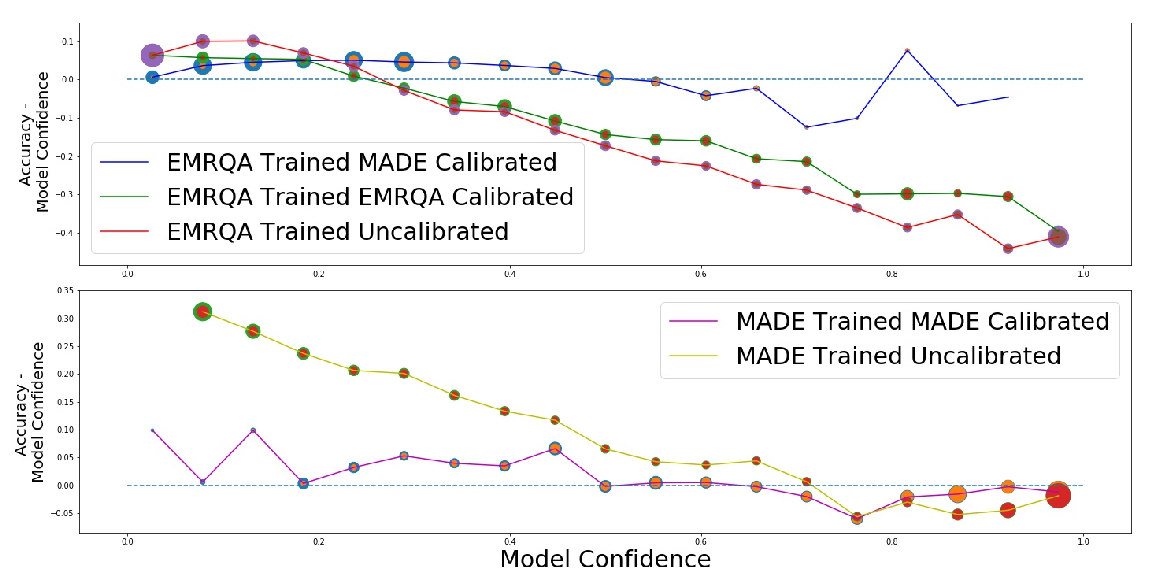
Calibrating Structured Output Predictors for Natural Language Processing
Abhyuday Jagannatha, Hong Yu,