Unsupervised Discourse Constituency Parsing Using Viterbi EM
Noriki Nishida, Hideki Nakayama
Discourse and Pragmatics TACL Paper
Session 11B: Jul 8
(06:00-07:00 GMT)

Session 12A: Jul 8
(08:00-09:00 GMT)

Abstract:
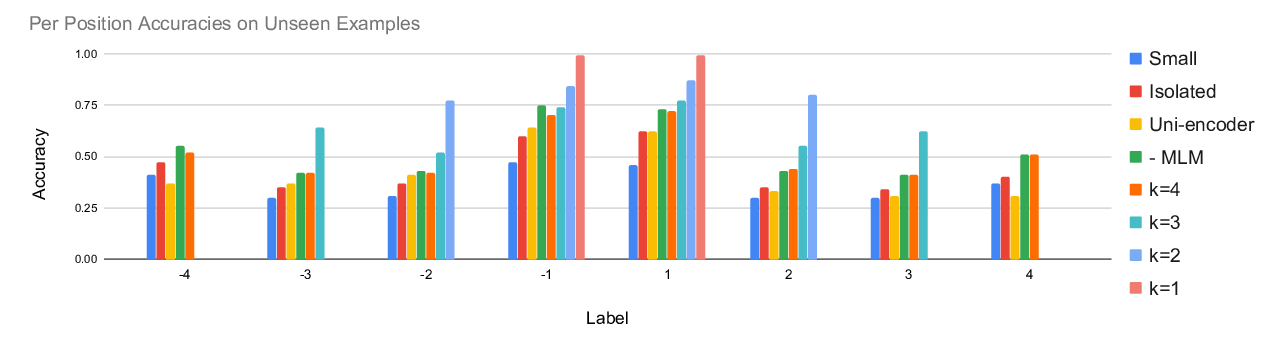
In this paper, we introduce an unsupervised discourse constituency parsing algorithm. We use Viterbi EM with a margin-based criterion to train a span-based discourse parser in an unsupervised manner. We also propose initialization methods for Viterbi training of discourse constituents based on our prior knowledge of text structures. Experimental results demonstrate that our unsupervised parser achieves comparable or even superior performance to fully supervised parsers. We also investigate discourse constituents that are learned by our method.
You can open the
pre-recorded video
in a separate window.
NOTE: The SlidesLive video may display a random order of the authors.
The correct author list is shown at the top of this webpage.
Similar Papers
A Complete Shift-Reduce Chinese Discourse Parser with Robust Dynamic Oracle
Shyh-Shiun Hung, Hen-Hsen Huang, Hsin-Hsi Chen,
An Empirical Comparison of Unsupervised Constituency Parsing Methods
Jun Li, Yifan Cao, Jiong Cai, Yong Jiang, Kewei Tu,
The Summary Loop: Learning to Write Abstractive Summaries Without Examples
Philippe Laban, Andrew Hsi, John Canny, Marti A. Hearst,
Pretraining with Contrastive Sentence Objectives Improves Discourse Performance of Language Models
Dan Iter, Kelvin Guu, Larry Lansing, Dan Jurafsky,