An Empirical Comparison of Unsupervised Constituency Parsing Methods
Jun Li, Yifan Cao, Jiong Cai, Yong Jiang, Kewei Tu
Syntax: Tagging, Chunking and Parsing Short Paper
Session 6A: Jul 7
(05:00-06:00 GMT)

Session 7A: Jul 7
(08:00-09:00 GMT)

Abstract:
Unsupervised constituency parsing aims to learn a constituency parser from a training corpus without parse tree annotations. While many methods have been proposed to tackle the problem, including statistical and neural methods, their experimental results are often not directly comparable due to discrepancies in datasets, data preprocessing, lexicalization, and evaluation metrics. In this paper, we first examine experimental settings used in previous work and propose to standardize the settings for better comparability between methods. We then empirically compare several existing methods, including decade-old and newly proposed ones, under the standardized settings on English and Japanese, two languages with different branching tendencies. We find that recent models do not show a clear advantage over decade-old models in our experiments. We hope our work can provide new insights into existing methods and facilitate future empirical evaluation of unsupervised constituency parsing.
You can open the
pre-recorded video
in a separate window.
NOTE: The SlidesLive video may display a random order of the authors.
The correct author list is shown at the top of this webpage.
Similar Papers
Harvesting and Refining Question-Answer Pairs for Unsupervised QA
Zhongli Li, Wenhui Wang, Li Dong, Furu Wei, Ke Xu,
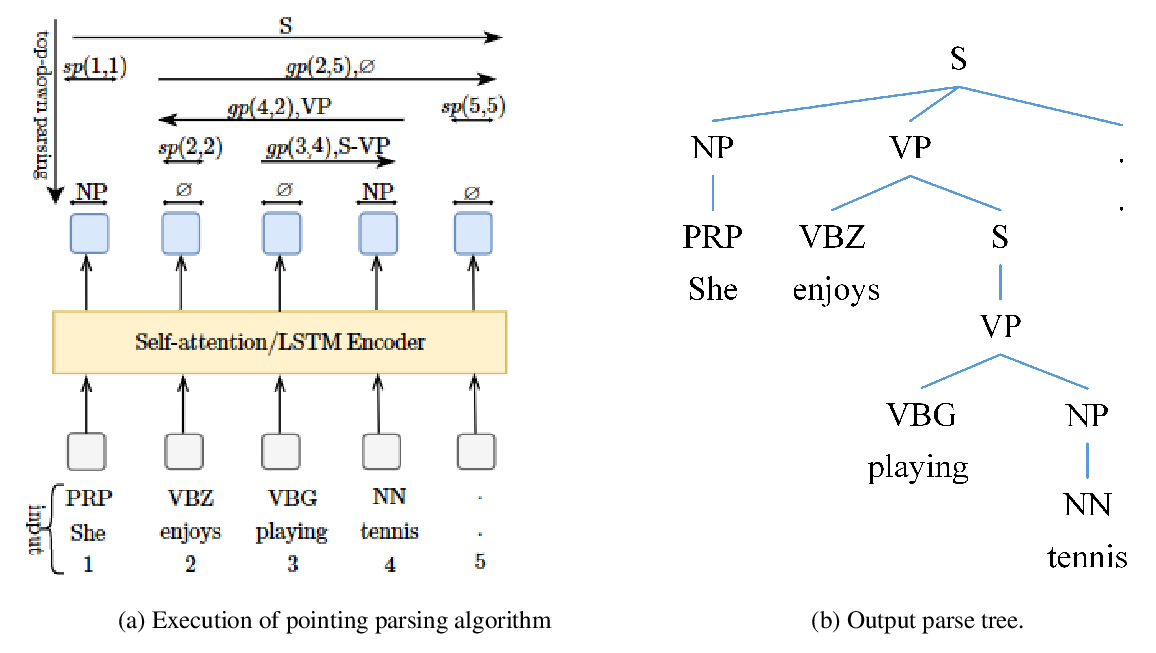
Efficient Constituency Parsing by Pointing
Thanh-Tung Nguyen, Xuan-Phi Nguyen, Shafiq Joty, Xiaoli Li,
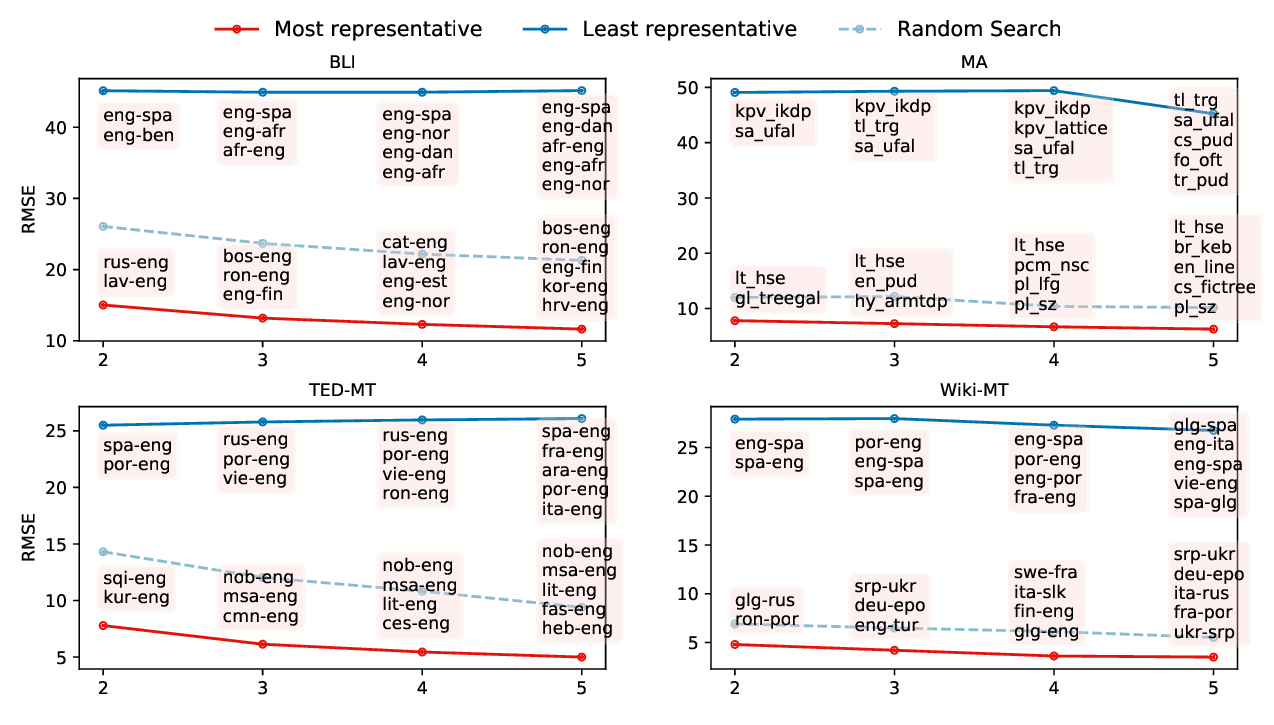
Predicting Performance for Natural Language Processing Tasks
Mengzhou Xia, Antonios Anastasopoulos, Ruochen Xu, Yiming Yang, Graham Neubig,