Self-Attention with Cross-Lingual Position Representation
Liang Ding, Longyue Wang, Dacheng Tao
Machine Translation Short Paper
Session 2B: Jul 6
(09:00-10:00 GMT)

Session 3A: Jul 6
(12:00-13:00 GMT)

Abstract:
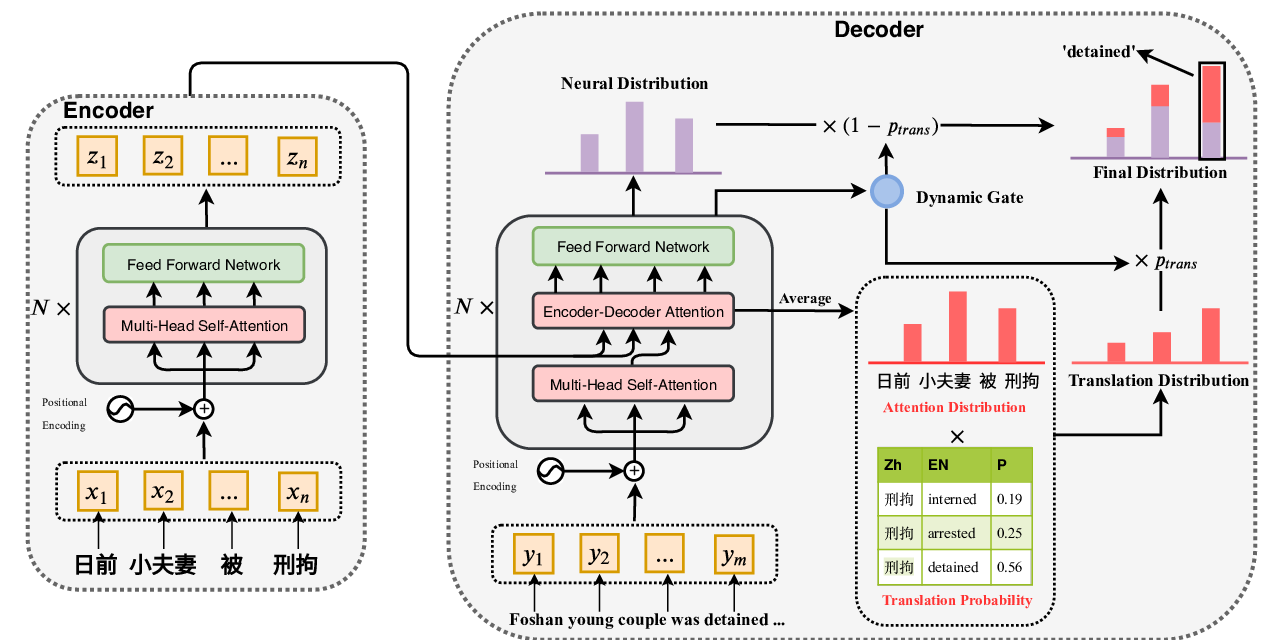
Position encoding (PE), an essential part of self-attention networks (SANs), is used to preserve the word order information for natural language processing tasks, generating fixed position indices for input sequences. However, in cross-lingual scenarios, \eg machine translation, the PEs of source and target sentences are modeled independently. Due to word order divergences in different languages, modeling the cross-lingual positional relationships might help SANs tackle this problem. In this paper, we augment SANs with cross-lingual position representations to model the bilingually aware latent structure for the input sentence. Specifically, we utilize bracketing transduction grammar (BTG)-based reordering information to encourage SANs to learn bilingual diagonal alignments. Experimental results on WMT'14 English⇒German, WAT'17 Japanese⇒English, and WMT'17 Chinese⇔English translation tasks demonstrate that our approach significantly and consistently improves translation quality over strong baselines. Extensive analyses confirm that the performance gains come from the cross-lingual information.
You can open the
pre-recorded video
in a separate window.
NOTE: The SlidesLive video may display a random order of the authors.
The correct author list is shown at the top of this webpage.
Similar Papers
Jointly Learning to Align and Summarize for Neural Cross-Lingual Summarization
Yue Cao, Hui Liu, Xiaojun Wan,
How Does Selective Mechanism Improve Self-Attention Networks?
Xinwei Geng, Longyue Wang, Xing Wang, Bing Qin, Ting Liu, Zhaopeng Tu,
Multilingual Universal Sentence Encoder for Semantic Retrieval
Yinfei Yang, Daniel Cer, Amin Ahmad, Mandy Guo, Jax Law, Noah Constant, Gustavo Hernandez Abrego, Steve Yuan, Chris Tar, Yun-hsuan Sung, Brian Strope, Ray Kurzweil,
Attend, Translate and Summarize: An Efficient Method for Neural Cross-Lingual Summarization
Junnan Zhu, Yu Zhou, Jiajun Zhang, Chengqing Zong,