Content Word Aware Neural Machine Translation
Kehai Chen, Rui Wang, Masao Utiyama, Eiichiro Sumita
Machine Translation Short Paper
Session 1A: Jul 6
(05:00-06:00 GMT)

Session 3B: Jul 6
(13:00-14:00 GMT)

Abstract:
Neural machine translation (NMT) encodes the source sentence in a universal way to generate the target sentence word-by-word. However, NMT does not consider the importance of word in the sentence meaning, for example, some words (i.e., content words) express more important meaning than others (i.e., function words). To address this limitation, we first utilize word frequency information to distinguish between content and function words in a sentence, and then design a content word-aware NMT to improve translation performance. Empirical results on the WMT14 English-to-German, WMT14 English-to-French, and WMT17 Chinese-to-English translation tasks show that the proposed methods can significantly improve the performance of Transformer-based NMT.
You can open the
pre-recorded video
in a separate window.
NOTE: The SlidesLive video may display a random order of the authors.
The correct author list is shown at the top of this webpage.
Similar Papers
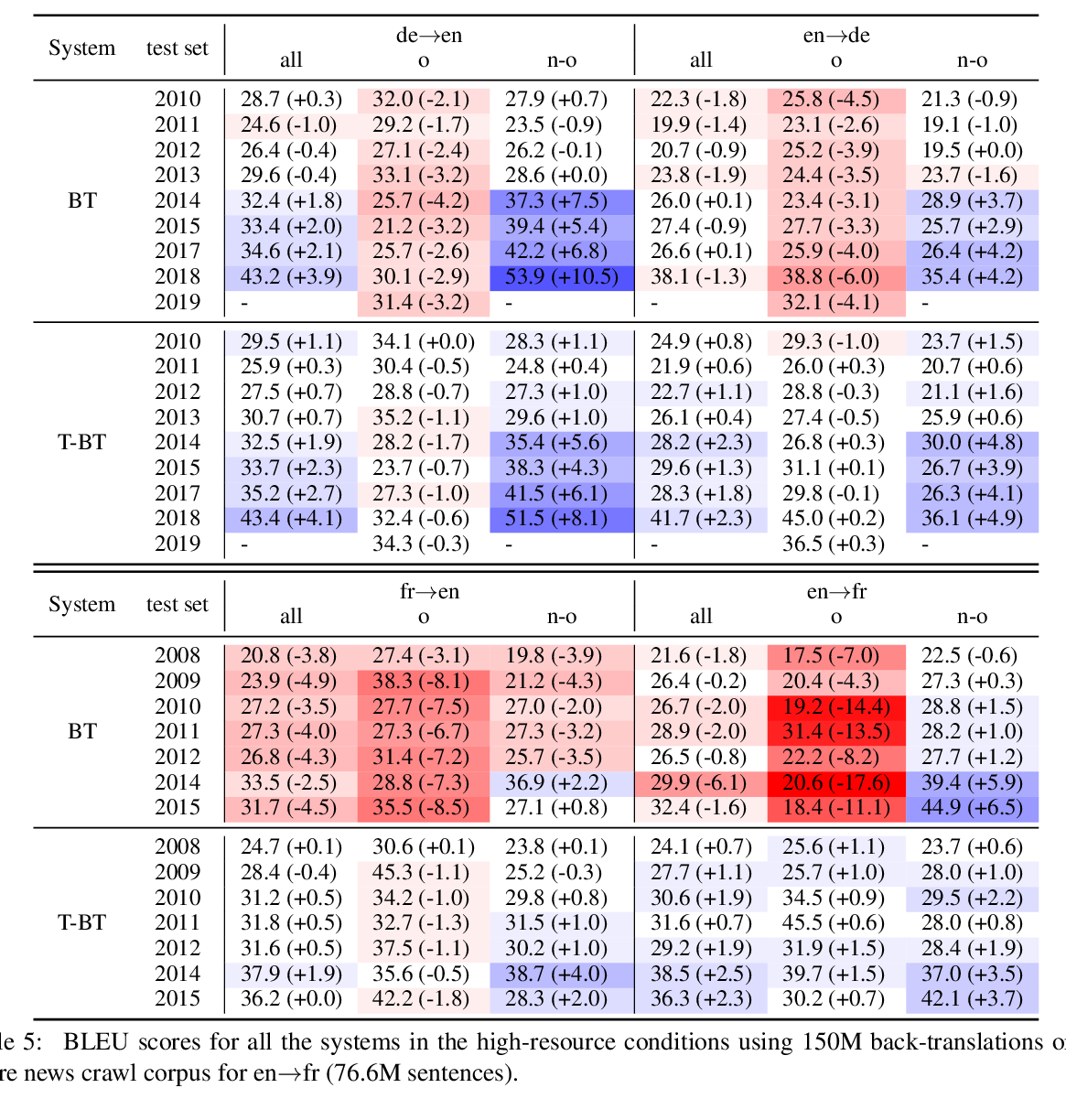
Norm-Based Curriculum Learning for Neural Machine Translation
Xuebo Liu, Houtim Lai, Derek F. Wong, Lidia S. Chao,
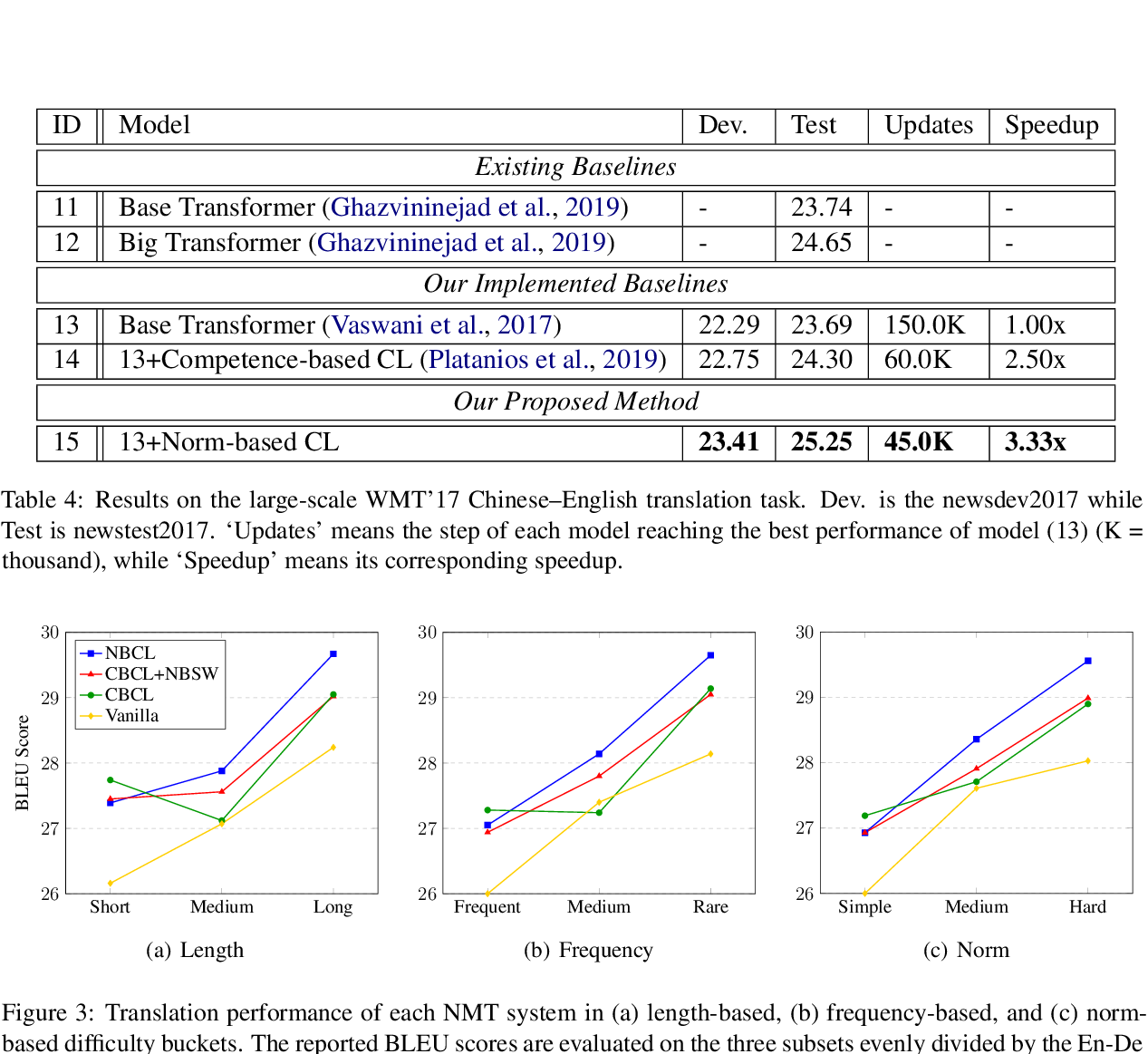
Multiscale Collaborative Deep Models for Neural Machine Translation
Xiangpeng Wei, Heng Yu, Yue Hu, Yue Zhang, Rongxiang Weng, Weihua Luo,
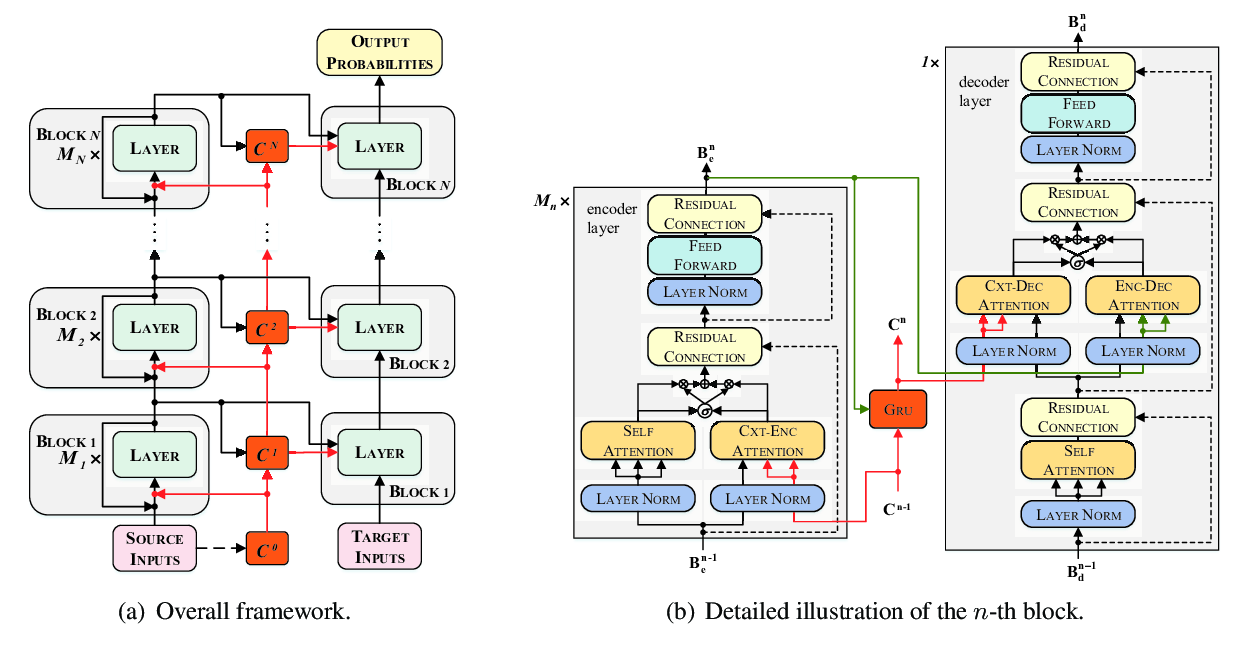
Multi-Task Neural Model for Agglutinative Language Translation
Yirong Pan, Xiao Li, Yating Yang, Rui Dong,
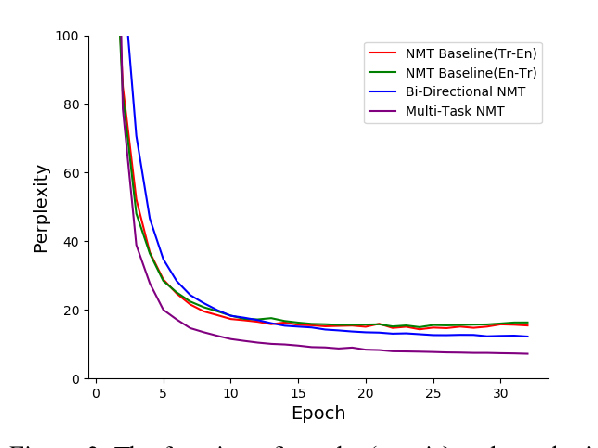
Tagged Back-translation Revisited: Why Does It Really Work?
Benjamin Marie, Raphael Rubino, Atsushi Fujita,