Multi-Granularity Interaction Network for Extractive and Abstractive Multi-Document Summarization
Hanqi Jin, Tianming Wang, Xiaojun Wan
Summarization Long Paper
Session 11A: Jul 8
(05:00-06:00 GMT)

Session 12A: Jul 8
(08:00-09:00 GMT)

Abstract:
In this paper, we propose a multi-granularity interaction network for extractive and abstractive multi-document summarization, which jointly learn semantic representations for words, sentences, and documents. The word representations are used to generate an abstractive summary while the sentence representations are used to produce an extractive summary. We employ attention mechanisms to interact between different granularity of semantic representations, which helps to capture multi-granularity key information and improves the performance of both abstractive and extractive summarization. Experiment results show that our proposed model substantially outperforms all strong baseline methods and achieves the best results on the Multi-News dataset.
You can open the
pre-recorded video
in a separate window.
NOTE: The SlidesLive video may display a random order of the authors.
The correct author list is shown at the top of this webpage.
Similar Papers
Leveraging Graph to Improve Abstractive Multi-Document Summarization
Wei Li, Xinyan Xiao, Jiachen Liu, Hua Wu, Haifeng Wang, Junping Du,
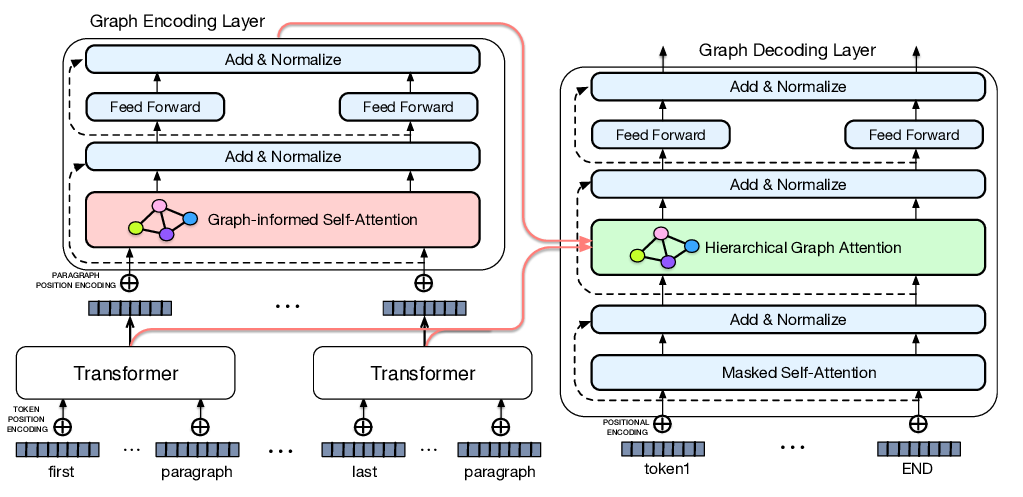
A Novel Graph-based Multi-modal Fusion Encoder for Neural Machine Translation
Yongjing Yin, Fandong Meng, Jinsong Su, Chulun Zhou, Zhengyuan Yang, Jie Zhou, Jiebo Luo,

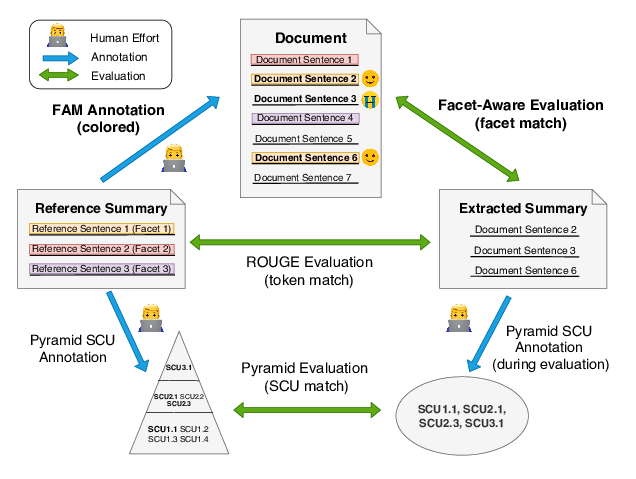
Facet-Aware Evaluation for Extractive Summarization
Yuning Mao, Liyuan Liu, Qi Zhu, Xiang Ren, Jiawei Han,
Optimizing the Factual Correctness of a Summary: A Study of Summarizing Radiology Reports
Yuhao Zhang, Derek Merck, Emily Tsai, Christopher D. Manning, Curtis Langlotz,