Improving Disfluency Detection by Self-Training a Self-Attentive Model
Paria Jamshid Lou, Mark Johnson
Speech and Multimodality Long Paper
Session 6B: Jul 7
(06:00-07:00 GMT)

Session 7B: Jul 7
(09:00-10:00 GMT)

Abstract:
Self-attentive neural syntactic parsers using contextualized word embeddings (e.g. ELMo or BERT) currently produce state-of-the-art results in joint parsing and disfluency detection in speech transcripts. Since the contextualized word embeddings are pre-trained on a large amount of unlabeled data, using additional unlabeled data to train a neural model might seem redundant. However, we show that self-training --- a semi-supervised technique for incorporating unlabeled data --- sets a new state-of-the-art for the self-attentive parser on disfluency detection, demonstrating that self-training provides benefits orthogonal to the pre-trained contextualized word representations. We also show that ensembling self-trained parsers provides further gains for disfluency detection.
You can open the
pre-recorded video
in a separate window.
NOTE: The SlidesLive video may display a random order of the authors.
The correct author list is shown at the top of this webpage.
Similar Papers
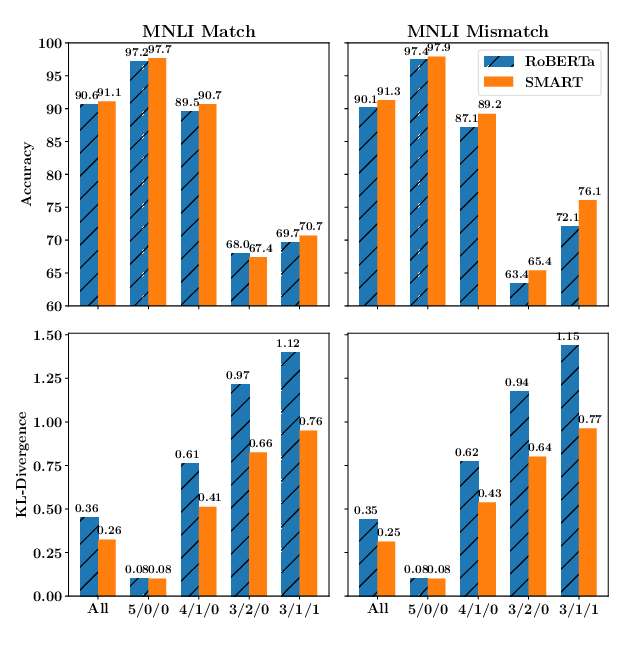
SMART: Robust and Efficient Fine-Tuning for Pre-trained Natural Language Models through Principled Regularized Optimization
Haoming Jiang, Pengcheng He, Weizhu Chen, Xiaodong Liu, Jianfeng Gao, Tuo Zhao,
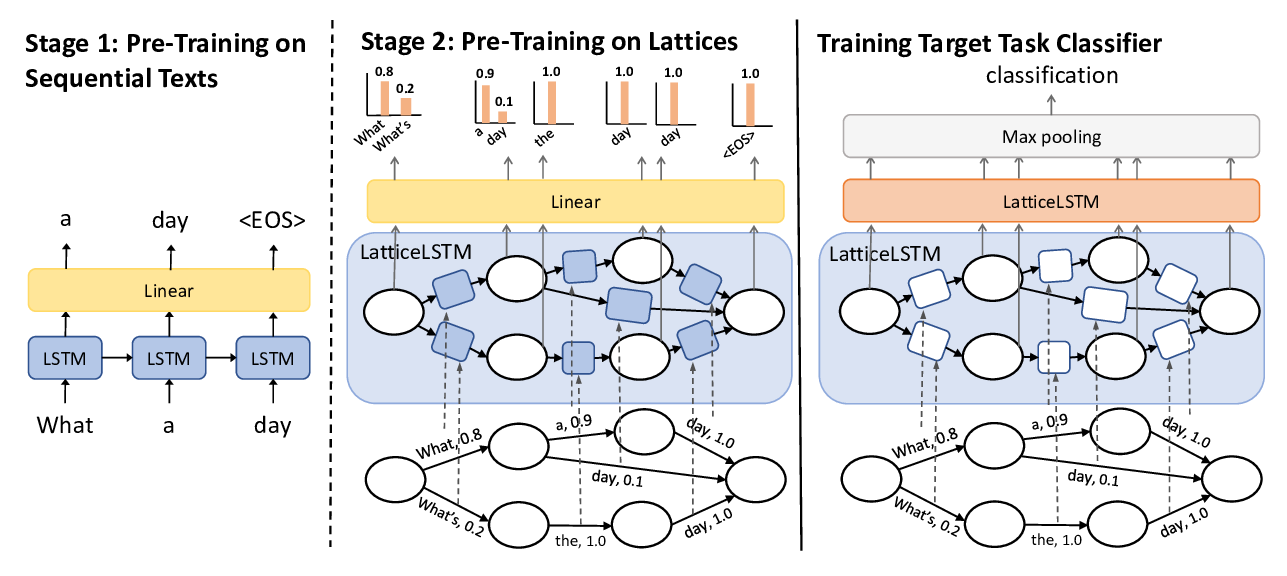
Learning Spoken Language Representations with Neural Lattice Language Modeling
Chao-Wei Huang, Yun-Nung Chen,