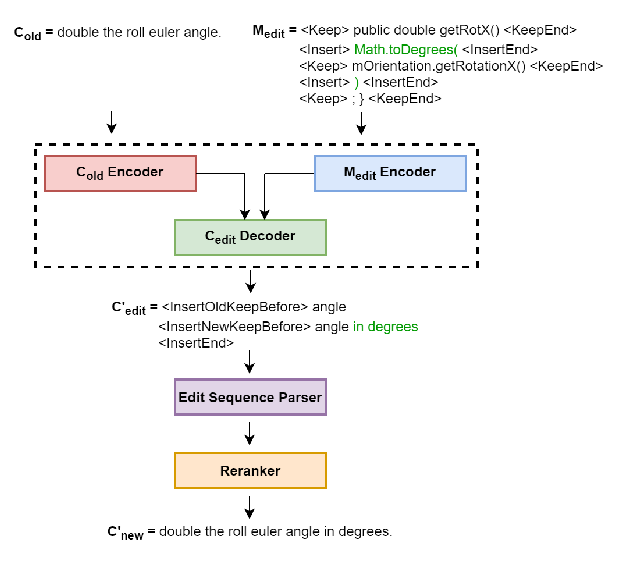
Analysing Lexical Semantic Change with Contextualised Word Representations
Mario Giulianelli, Marco Del Tredici, Raquel Fernández
Semantics: Lexical Long Paper
Session 7A: Jul 7
(08:00-09:00 GMT)

Session 8A: Jul 7
(12:00-13:00 GMT)

Abstract:
This paper presents the first unsupervised approach to lexical semantic change that makes use of contextualised word representations. We propose a novel method that exploits the BERT neural language model to obtain representations of word usages, clusters these representations into usage types, and measures change along time with three proposed metrics. We create a new evaluation dataset and show that the model representations and the detected semantic shifts are positively correlated with human judgements. Our extensive qualitative analysis demonstrates that our method captures a variety of synchronic and diachronic linguistic phenomena. We expect our work to inspire further research in this direction.
You can open the
pre-recorded video
in a separate window.
NOTE: The SlidesLive video may display a random order of the authors.
The correct author list is shown at the top of this webpage.
Similar Papers
Finding Universal Grammatical Relations in Multilingual BERT
Ethan A. Chi, John Hewitt, Christopher D. Manning,
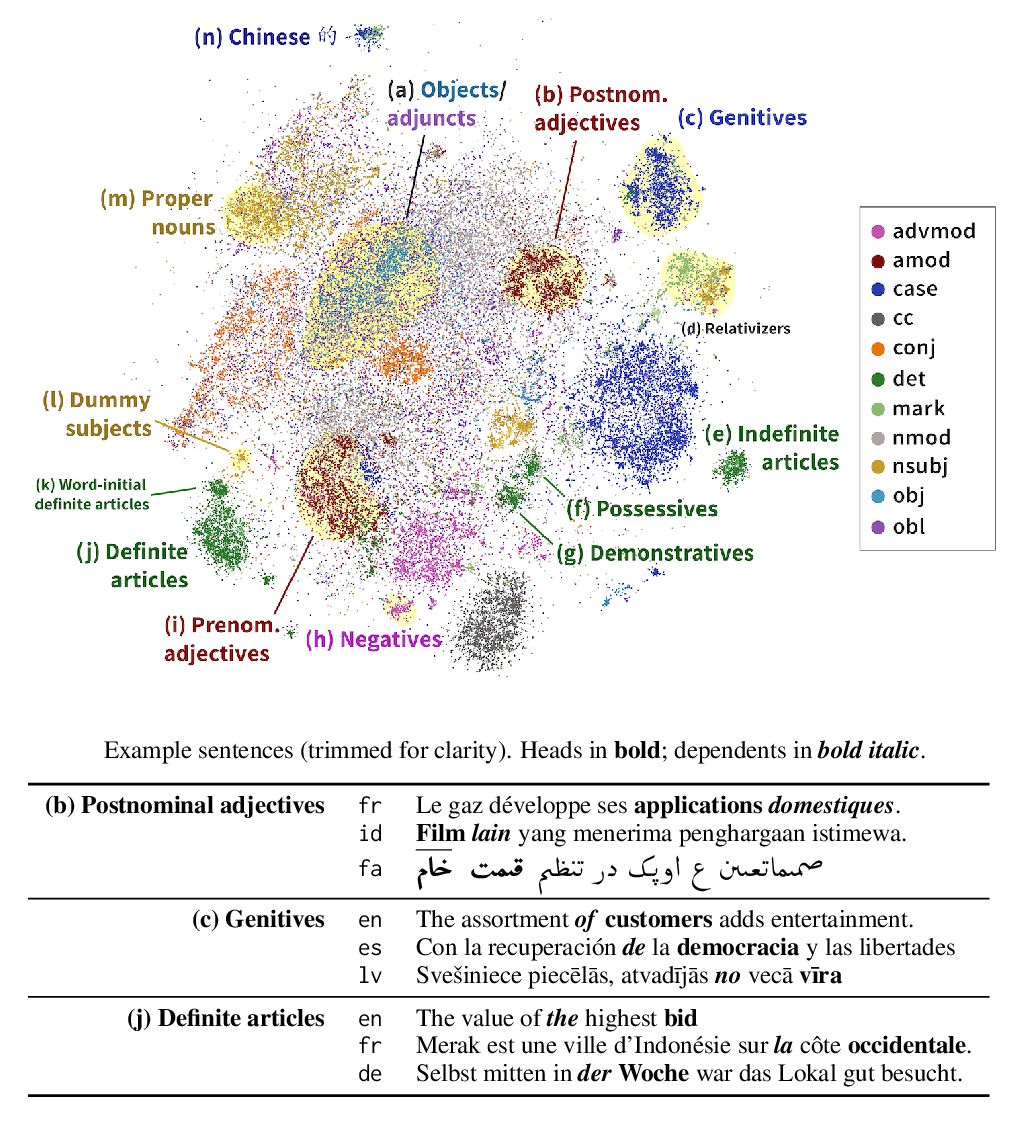
An Empirical Comparison of Unsupervised Constituency Parsing Methods
Jun Li, Yifan Cao, Jiong Cai, Yong Jiang, Kewei Tu,
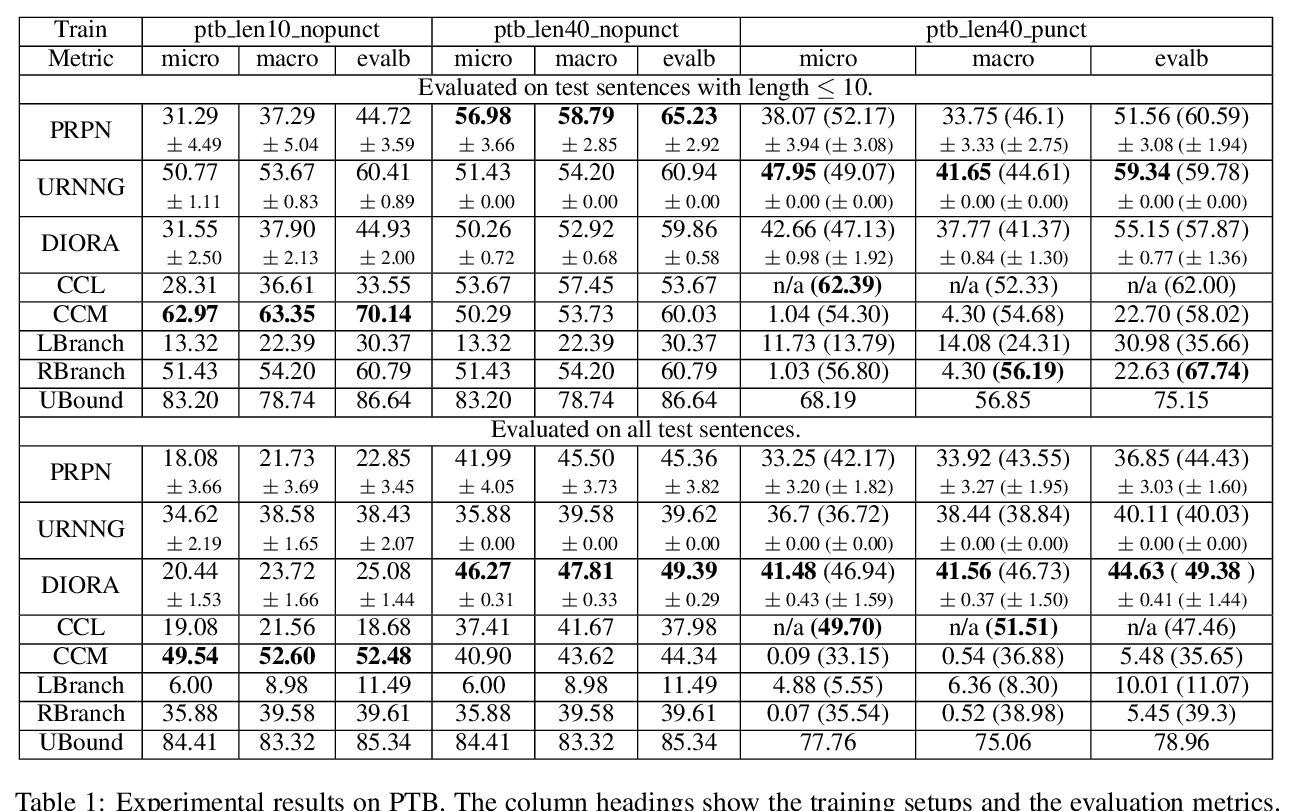
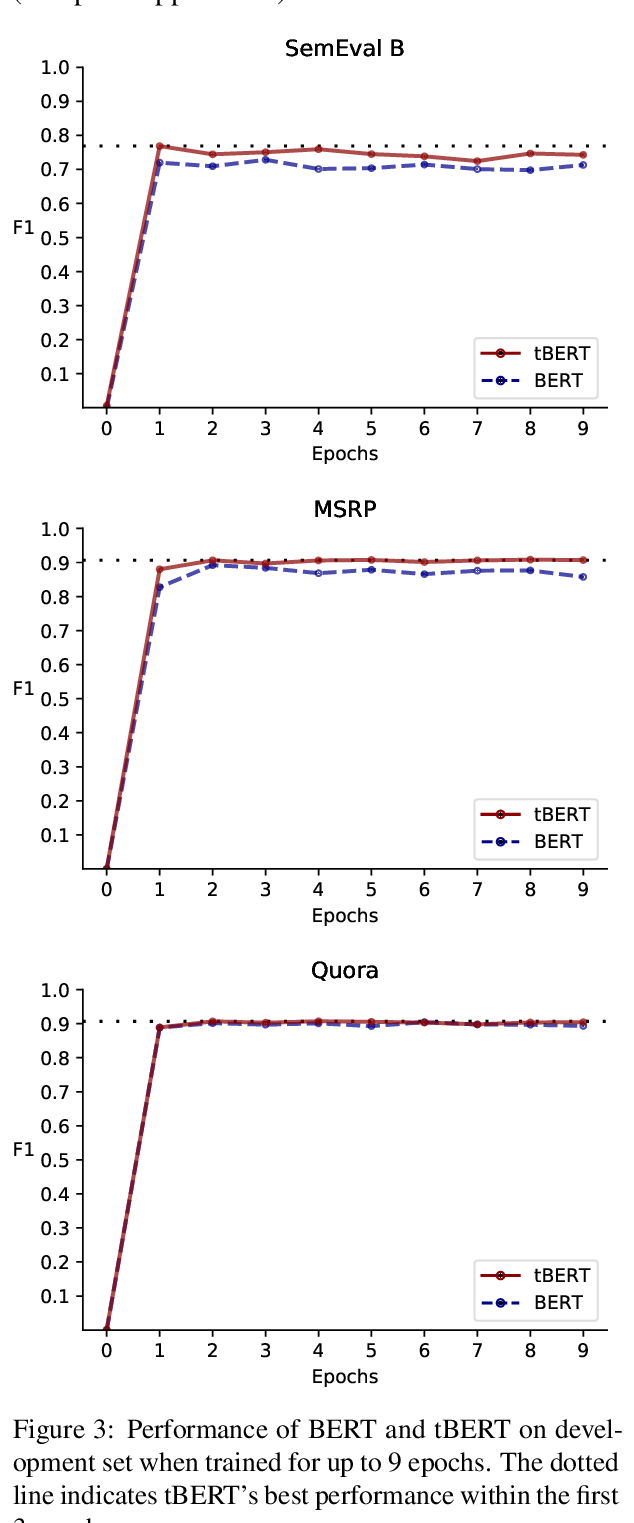
tBERT: Topic Models and BERT Joining Forces for Semantic Similarity Detection
Nicole Peinelt, Dong Nguyen, Maria Liakata,
Learning to Update Natural Language Comments Based on Code Changes
Sheena Panthaplackel, Pengyu Nie, Milos Gligoric, Junyi Jessy Li, Raymond Mooney,