Improving Chinese Word Segmentation with Wordhood Memory Networks
Yuanhe Tian, Yan Song, Fei Xia, Tong Zhang, Yonggang Wang
Phonology, Morphology and Word Segmentation Long Paper
Session 14A: Jul 8
(17:00-18:00 GMT)

Session 15B: Jul 8
(21:00-22:00 GMT)

Abstract:
Contextual features always play an important role in Chinese word segmentation (CWS). Wordhood information, being one of the contextual features, is proved to be useful in many conventional character-based segmenters. However, this feature receives less attention in recent neural models and it is also challenging to design a framework that can properly integrate wordhood information from different wordhood measures to existing neural frameworks. In this paper, we therefore propose a neural framework, WMSeg, which uses memory networks to incorporate wordhood information with several popular encoder-decoder combinations for CWS. Experimental results on five benchmark datasets indicate the memory mechanism successfully models wordhood information for neural segmenters and helps WMSeg achieve state-of-the-art performance on all those datasets. Further experiments and analyses also demonstrate the robustness of our proposed framework with respect to different wordhood measures and the efficiency of wordhood information in cross-domain experiments.
You can open the
pre-recorded video
in a separate window.
NOTE: The SlidesLive video may display a random order of the authors.
The correct author list is shown at the top of this webpage.
Similar Papers
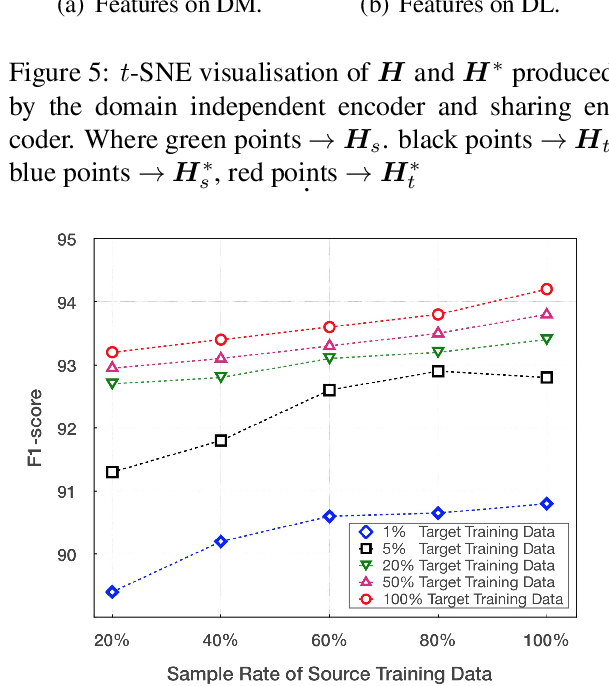
Learning to Tag OOV Tokens by Integrating Contextual Representation and Background Knowledge
Keqing He, Yuanmeng Yan, Weiran XU,
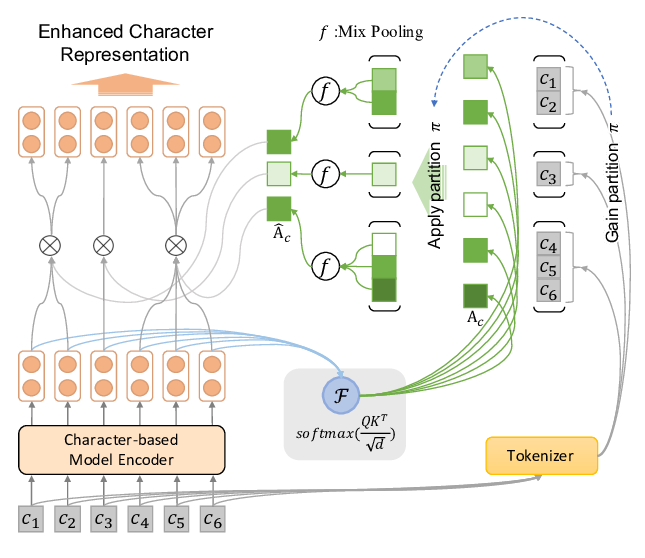
Enhancing Pre-trained Chinese Character Representation with Word-aligned Attention
Yanzeng Li, Bowen Yu, Xue Mengge, Tingwen Liu,
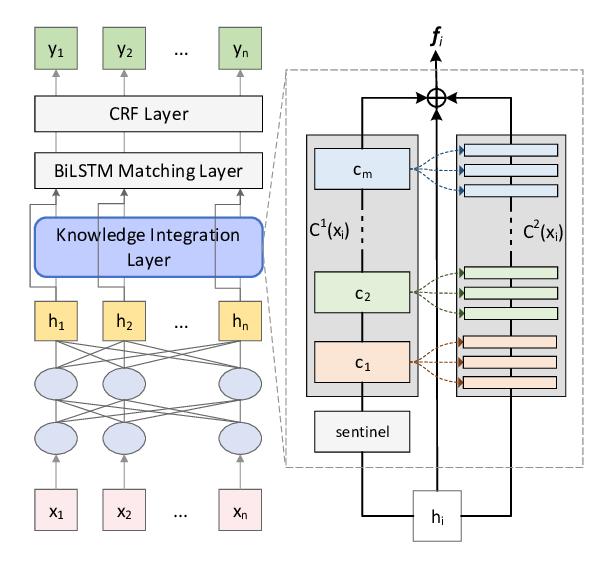
Coupling Distant Annotation and Adversarial Training for Cross-Domain Chinese Word Segmentation
Ning Ding, Dingkun Long, Guangwei Xu, Muhua Zhu, Pengjun Xie, Xiaobin Wang, Haitao Zheng,
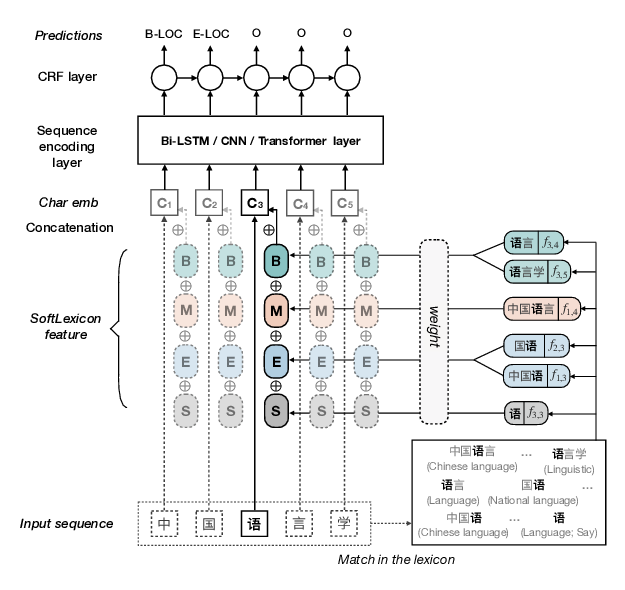
Simplify the Usage of Lexicon in Chinese NER
Ruotian Ma, Minlong Peng, Qi Zhang, Zhongyu Wei, Xuanjing Huang,